Navigating the Digital Shift: A New Era for Healthcare Professionals
- Milley Carrol, MBA, MHC

- Feb 13, 2025
- 6 min read
Updated: Feb 16, 2025

The digital shift presents both challenges and opportunities for healthcare professionals. While we must adapt to new technologies and working methods, these advancements ultimately improve patient care, increase efficiency, and expand access to healthcare services.
Takeaways:
Digital tools are reshaping healthcare delivery, requiring professionals to acquire new skills.
Telehealth is expanding access to care but demands adjustments in patient interaction.
Data analytics provides powerful insights for patient care, and understanding these insights has become mandatory.
Cybersecurity is a growing concern, and protecting patient data is a top priority.
Continuous learning is needed to keep pace with the evolving technological landscape.
As a healthcare business analyst at BioLife Health Research Center, I've witnessed firsthand the profound impact of technology on our industry. The digital shift isn't on the horizon; it's reshaping how we deliver care, interact with patients, and manage information.
This article explores the key changes technology is introducing to the delivery of healthcare professionals' services. It will cover some of the tools used and how to adopt these changes in your workplace.
1. The Rise of Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
Telehealth has moved beyond occasional video calls to become a cornerstone of modern healthcare. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) devices, such as wearable sensors and smart home devices, provide a constant stream of patient data.
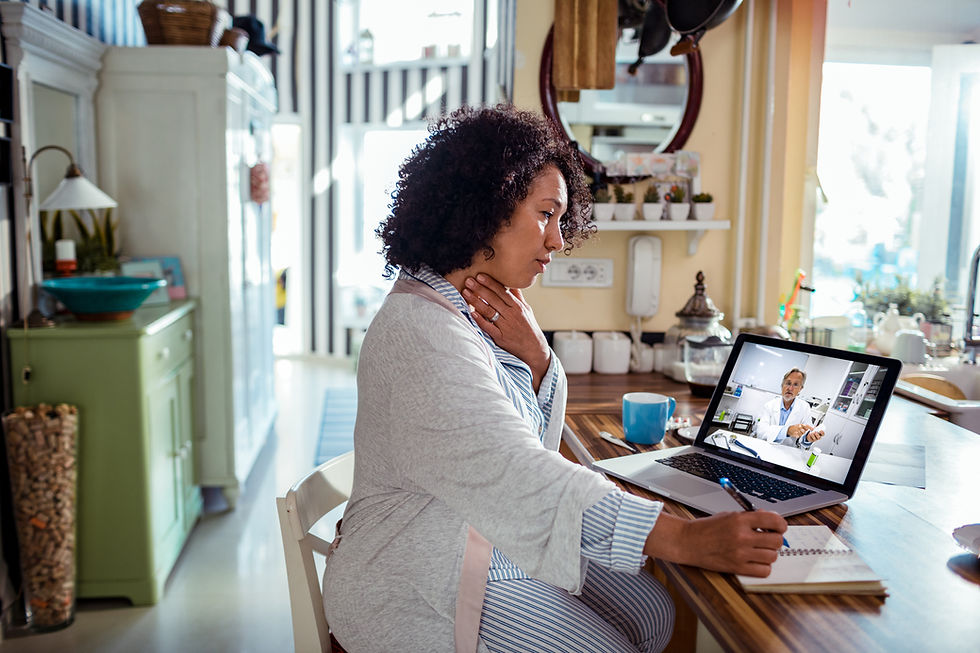

What it means for us: We must become proficient in virtual consultations, learn to interpret data from RPM devices, and develop strategies for managing patient care remotely. This includes adjusting our communication styles for virtual interactions and learning to troubleshoot technical issues.
Real-world example: A cardiologist can now remotely monitor a patient's heart rhythm using a wearable ECG patch. This allows for early detection of abnormalities and timely intervention, potentially preventing serious cardiac events. I had a colleague, Juan, who was initially hesitant about telehealth. However, he became a strong advocate after seeing how it allowed him to connect with patients in rural areas with limited access to specialized care.
Facts: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), telehealth use increased by 154% in the last week of March 2024 compared to the same period in 2019. The American Hospital Association (AHA) reports that 76% of U.S. hospitals use telehealth technology to connect with patients and consulting practitioners.
2. Data Analytics and Clinical Decision Support
Big data is no longer a buzzword; it's a reality in healthcare. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and data from various sources provide a wealth of information. Clinical Decision Support (CDS) systems use this data to offer evidence-based recommendations to clinicians.
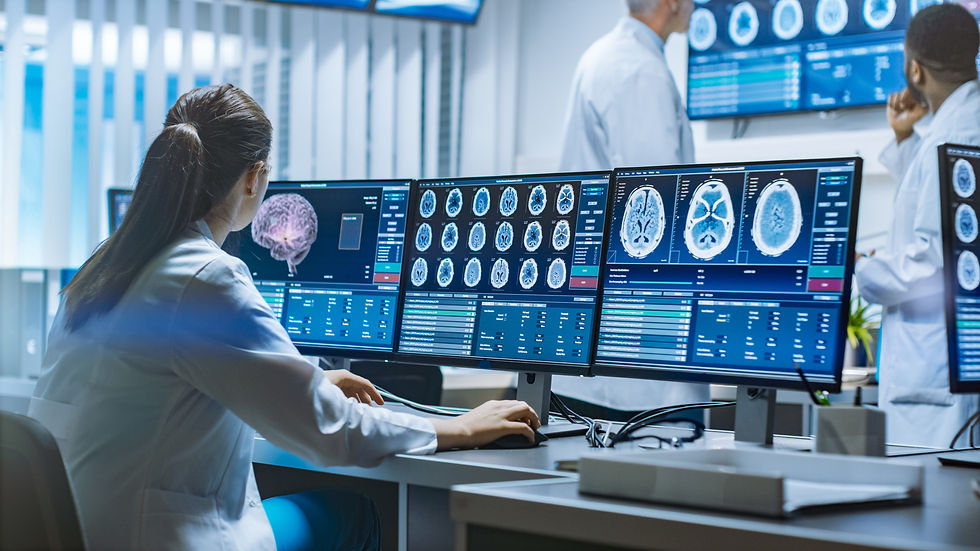
What it means for us: We're becoming data interpreters. We need to understand how to analyze trends, identify patterns, and use data-driven insights to improve patient outcomes. This involves learning basic data literacy skills and understanding the capabilities of CDS systems.
Real-world example: A hospital can use predictive analytics to identify patients at high risk of readmission. By analyzing factors such as age, comorbidities, and previous hospitalizations, they can target interventions to support these patients and prevent future readmissions. I've seen this firsthand at BioLife, where we use data analytics to optimize patient flow and reduce clinic wait times.
Facts: A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association (JAMIA) found that CDS systems can reduce medication errors by up to 83%. Another study in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that data analytics could predict sepsis, a life-threatening condition, up to 24 hours before clinical signs appear.
3. Enhanced Cybersecurity Threats
With the increased reliance on digital systems comes a greater risk of cyberattacks. Healthcare data is highly valuable on the black market, making healthcare organizations prime targets for hackers.

What it means for us: We are now on the front lines of cybersecurity. We must protect patient data, adhere to security protocols, and recognize potential threats like phishing scams.
Real-world example: A ransomware attack on a hospital can cripple its operations, preventing access to patient records and disrupting critical care. This happened to a hospital in a neighboring state, causing significant disruption and financial losses. The incident served as a wake-up call for many regional healthcare organizations.
Facts: According to the HIPAA Journal, 642 large-scale healthcare data breaches were reported in 2024, affecting over 29 million patient records. According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of a healthcare data breach is $7.13 million.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming diagnostics, treatment planning, and administrative tasks. AI-powered image analysis tools can detect subtle anomalies in medical images, while ML algorithms can personalize treatment plans based on patient characteristics.

What it means for us: AI is becoming our colleague. We need to understand the capabilities and limitations of AI tools, learn to collaborate with AI systems, and remain adaptable as AI takes on more routine tasks.
Real-world example: AI-powered chatbots can handle appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and basic patient inquiries, freeing staff to focus on more complex tasks. My team is currently exploring implementing an AI-powered system to automate the prior authorization process for medications, which is a very time-consuming manual task.
Facts: A study published in The Lancet Digital Health found that AI algorithms could diagnose breast cancer from mammograms with accuracy comparable to that of experienced radiologists. McKinsey estimates that AI could potentially create $350 billion to $410 billion in value annually for the healthcare industry.
5. The Importance of Continuous Learning
The digital landscape is constantly evolving. New technologies, tools, and threats emerge regularly. To thrive in this environment, we must commit to lifelong learning.

What it means for us: We need to be proactive in seeking out training opportunities, attending webinars and conferences, and staying updated on the latest advancements in healthcare technology. This could involve learning new software, understanding new regulations, or developing new skills.
Real-world example: Many professional healthcare organizations now offer certifications in health informatics, telehealth, and cybersecurity. Pursuing these certifications can demonstrate our commitment to staying current and enhance our career prospects.
Final Thought
The digital transformation of healthcare is not just about technology; it's about people. It's about using technology to improve our patients' lives and support healthcare professionals' work. As we move forward, let's focus on the human element of healthcare, using technology to enhance, not replace, the caring and compassionate approach that defines our profession.
We can successfully navigate this new era by embracing change, committing to continuous learning, and focusing on patient-centered care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What if I'm not tech-savvy? How can I possibly keep up with all these changes?
Many resources are available to help healthcare professionals develop their digital skills. Start with small steps, such as taking online courses or attending workshops. Focus on the technologies most relevant to your specific role and practice setting.
How can I protect myself from becoming overwhelmed by the constant influx of new technologies?
Prioritize learning and focus on the areas that directly impact your daily work. Don't feel you need to master every new technology. Collaborate with colleagues, share knowledge, and seek support from your IT department.
How can I balance using technology with maintaining a personal connection with my patients?
It's important not to let technology overshadow the human element of healthcare. Use technology to enhance, not replace, face-to-face interactions. Make eye contact, listen actively, and show empathy, whether you're interacting in person or virtually.
What are some practical tips for improving my telehealth consultations?
It has good lighting, a quiet environment, and a stable internet connection. Practice using the telehealth platform beforehand, and have a backup plan in case of technical issues.
Where can I find reliable information about the latest healthcare technology trends?Follow reputable healthcare organizations in your specialty, such as the American Medical Association (AMA), the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), and professional organizations. Read industry publications and attend webinars and conferences.
About Milley Carrol, MBA, MHA
I'm a BioLife Health Research Center healthcare business analyst focused on optimizing medical processes and patient care systems. I lead teams to streamline operations, from patient flow to health records management. My expertise lies in developing cost-effective solutions that enhance healthcare efficiency. I aim to improve patient outcomes and organizational performance in healthcare by applying data-driven insights. Follow me on LinkedIn.



