A New Era of Hope: Breakthroughs in Mental Health Treatment
- Sara Johnson, BA, Psy

- Aug 15, 2025
- 6 min read

How Emerging Therapies Are Moving Beyond the Traditional to Offer New Pathways to Wellness

The promising new frontiers of mental health treatment in the US, from psychedelic-assisted therapies to advanced technologies and community-based models, are offering hope and clarity for patients and their families.
Takeaways
New treatments are moving beyond traditional talk therapy and pharmacology.
Psychedelic-assisted therapies (MDMA, psilocybin) are showing promise for treatment-resistant conditions.
Technologies like TMS and digital therapeutics offer targeted, non-invasive options.
Emerging models like social prescribing address the community and lifestyle aspects of mental health.
The future of mental healthcare is about personalized, multi-faceted approaches.
What if the map to mental wellness is expanding, revealing new, promising pathways we never thought possible? For many who feel they've exhausted their options, the landscape of mental healthcare can feel discouragingly small. This article matters because it brings news from the frontier—a place of dedicated research, innovative technology, and renewed hope. It’s an exploration of emerging treatments that are transforming lives, providing powerful new tools for healing, and reshaping our understanding of what it means to care for the mind.
Introduction
From my perspective as a researcher and advocate in healthcare, I’ve never witnessed a more dynamic and hopeful moment in mental health. For decades, the primary tools in our toolkit have been talk therapy and psychotropic medications—both of which have provided immense relief for millions. Yet, we know they are not a perfect fit for everyone.
Today, a new chapter is being written. Driven by advancements in neuroscience, technology, and a deeper understanding of human consciousness, a wave of emerging treatments is creating new possibilities. This exploration isn't about miracle cures, but about illuminating the new, science-backed paths that are offering hope and tangible success, helping individuals construct new frameworks for well-being.
The Clinical Renaissance: Psychedelic-Assisted Therapies
Once relegated to the counter-culture, certain psychedelic compounds are now at the forefront of clinical research, showing remarkable potential for conditions that have been notoriously difficult to treat. It's crucial to understand this isn't about recreational use; it's about using these substances in a controlled, therapeutic setting with trained professionals.
MDMA-Assisted Therapy: Primarily studied for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), this therapy involves a patient taking a clinical dose of MDMA while guided by two therapists through an extended session. The substance appears to lower the brain's fear response, allowing individuals to revisit and process traumatic memories without being overwhelmed. It helps build a bridge of safety to the most difficult parts of one's story.
Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy: Psilocybin, the compound found in "magic mushrooms," is being studied for treatment-resistant depression and end-of-life anxiety. It seems to work by quiet-storming the brain's "Default Mode Network," which is often overactive in depression, characterized by rigid, ruminating thought patterns. Psilocybin can temporarily disrupt these patterns, allowing for new insights and perspectives, which can then be integrated with a therapist's guidance. The goal isn't just a chemical change, but a change in our very motivation and emotional regulation.
Real-life Story: "John," a veteran who struggled for years with debilitating PTSD, described his experience with MDMA-assisted therapy not as erasing his trauma, but as "finally being able to look at it without it consuming me." It gave him the perspective he needed to see it as part of his story, not the entirety of it —a crucial step in embracing imperfection for personal growth. |
Precision Medicine for the Mind: Advanced Technologies
This new era is also marked by technologies that can interact with the brain's specific circuits with incredible precision, offering non-invasive alternatives to medication.
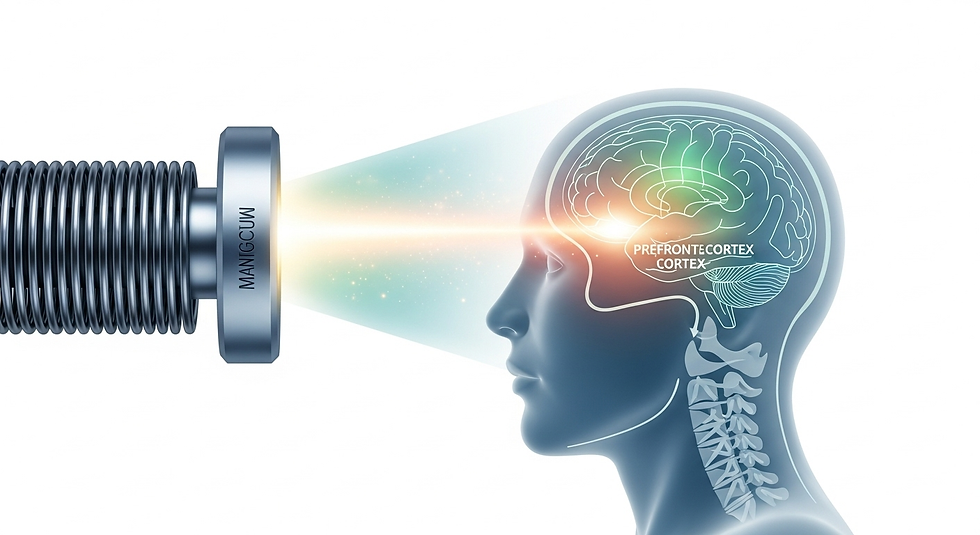
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): For individuals with major depression who haven't found relief with antidepressants, TMS is a groundbreaking option. The patient sits in a chair while a device uses targeted magnetic pulses to gently stimulate underactive areas of the brain associated with mood regulation, particularly the prefrontal cortex.
If depression sometimes feels like a specific part of your brain's orchestra is asleep, TMS is like a gentle conductor's tap on the music stand, waking those instruments up so they can rejoin the symphony.
Digital Therapeutics (DTx): These are prescription-strength software applications and virtual reality (VR) programs designed to treat specific conditions. For example, there are VR programs that provide exposure therapy for phobias in a safe, controlled environment, and apps that deliver cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia or anxiety. This is a powerful way to make mindfulness and mental clarity accessible.
The Power of Connection: Emerging Social Models
One of the most compassionate developments recognizes that mental health is not just about brain chemistry; it’s about our environment and our connections.
Social Prescribing: This innovative model, gaining traction in the US after success in the UK, allows healthcare providers to "prescribe" non-clinical, community-based activities. A doctor might prescribe joining a community gardening group for someone experiencing loneliness, an art class for someone with depression, or a hiking group for someone with anxiety. It directly addresses the social determinants of health, recognizing the profound truth that sometimes the best medicine is a sense of purpose and belonging. It’s a real-world application of the ideas discussed in the importance of community for mental health.
Real-life Story: An elderly woman named "Margaret," feeling deeply isolated after the loss of her spouse, was "prescribed" by her nurse practitioner to a local choir for seniors. She later said, "The music saved me, but the people… the people gave me a reason to get up in the morning." This powerfully illustrates how we can combat the loneliness epidemic. |
Summary
The future of mental healthcare is bright and multifaceted. From the profound, consciousness-shifting potential of psychedelic-assisted therapies to the precision of technologies like TMS and the compassionate, community-focused approach of social prescribing, the toolkit for healing is expanding rapidly. These emerging treatments offer new hope for those who have felt stuck, validating the idea that there is no one-size-fits-all solution and that the path to wellness is a deeply personal, developmental journey.
This new frontier in mental health is more than just new science; it’s a profound expression of our growing commitment to human dignity and well-being. It’s a testament to our persistence in seeking answers and our ability to create new ways to heal. For anyone on this journey—as a patient, caregiver, or advocate—this is a moment to be informed, to ask questions, and to hold onto a renewed sense of hope. New paths are opening every day.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I find out if I'm a candidate for these new treatments?
The first step is always to speak with a qualified mental health professional or your primary care doctor. They can assess your specific situation and discuss whether these emerging therapies might be appropriate and available in your area.
Are these treatments safe and regulated?
Psychedelic-assisted therapies are currently only legally available in rigorous clinical trials under FDA oversight. TMS is an FDA-approved treatment for depression and other conditions. Always ensure any treatment you seek is offered by a licensed and reputable provider.
Will my insurance cover these new therapies?
Coverage is evolving. TMS is now covered by many major insurance plans for specific conditions. Coverage for prescription digital therapeutics is growing. As psychedelic therapies move closer to full FDA approval, conversations about insurance coverage will become more concrete.
How are these approaches different from traditional therapy?
While traditional therapy often focuses on changing thought patterns over time, many of these new treatments work on a more foundational level—by directly altering brain activity (TMS), disrupting rigid neural pathways (psychedelics), or changing one's environment (social prescribing). They are often used in conjunction with talk therapy.
What if these treatments aren't available near me yet?
The field is moving quickly. You can stay informed by following reputable sources like the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and advocacy groups. Additionally, focus on what you can access, such as building community connections, which is a core principle of social prescribing.
Sources
Mitchell, J. M., Bogenschutz, M., Lilienstein, A., et al. (2021). MDMA-assisted therapy for severe PTSD: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Nature Medicine, 27(6), 1025–1033.
Gukasyan, N., Davis, A. K., Barrett, F. S., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of psilocybin-assisted treatment for major depressive disorder: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry, 79(4), 313–322.
National Institute of Mental Health. (n.d.). Brain Stimulation Therapies.
Tierney, S., & Fix, G. M. (2022). A Scoping Review of Social Prescribing in the United States. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 63(5), 779-788.
About Sara Johnson, BA Psy
As a Healthcare Advocacy and Community Wellness Specialist Sara brings compassionate research and practical advocacy to healthcare access. With a Master's in Public Health and 15 years of experience, she transforms individual empathy into systemic change, challenging audiences to view healthcare as a fundamental human right and collective responsibility.



